How to Design EAA-Compliant Accessible Websites
Digital Accessibility
Updated on February 13, 2025
Creating accessible websites is no longer just a nice-to-have—it’s essential. With the European Accessibility Act (EAA), European businesses must meet strict accessibility standards by June 2025.
The legislation aims to ensure equal access to content for everyone, including people with visual impairments, cognitive impairments, or those using assistive technologies like screen readers. For e-commerce websites, your site’s accessibility directly impacts the user experience, your search rankings, and your business’s success.
But why does website accessibility matter? Beyond simply complying with the law, building accessible web pages benefits everyone.
A well-designed site with keyboard navigation, proper use of alt text, and clear page titles allows more users, including assistive technology users, to navigate your content easily. That translates to more engagement, higher customer satisfaction, and a better reputation for your brand.
For example, adding descriptive alternative text to images helps screen reader users understand visual content while improving SEO. Offering multilingual video subtitles and high-contrast text ensures everyone can access your content, no matter their needs.
By incorporating accessibility features early on, web designers can avoid future headaches while improving the experience for all website visitors. Let’s look at some stunning websites that serve as examples to inspire your accessible web design journey.

How Accessible is Your Content? Find Out with This Free Checklist!
Download NowWhat is Web Accessibility?
Web accessibility is the concept of ensuring websites can be used by everyone, regardless of ability or disability. Whether someone has a visual impairment, relies on screen readers, or needs assistance navigating with keyboard accessibility, a well-designed accessible website should offer an inclusive experience.
Furthermore, there are now legal requirements surrounding web accessibility, like the EAA. Luckily, we created a video outlining the requirements – you can see the preview below:
Download the full video to learn more about the EAA
Essentially, web accessibility is making sure your content can be consumed by everyone, and that your website is navigable using accessibility tools.
Defining Web Accessibility
Web accessibility is creating digital spaces that work for everyone, including those with disabilities. This includes users relying on assistive technologies like screen readers, speech input software, or other tools to interact with websites.
An accessible website adapts to users’ diverse needs, offering functionality through keyboard navigation, ensuring text is understandable, and providing alternative text (alt text) for images so that screen reader users can grasp the content.
Why is this important? Think about the variety of ways people use the web—some navigate with the tab key instead of a mouse, while others need high contrast or large font sizes due to visual impairments. When you make your website accessible, you are catering to a broader audience, offering an inclusive experience that can boost user engagement and trust.
Key Principles of Web Accessibility
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) set the standards for web accessibility and help businesses understand what it takes to create an inclusive digital space. These guidelines focus on four fundamental principles:
- Perceivable: Content should be easy to see and hear, accommodating users with visual impairments through options like alt text, captions for videos, and adaptable page layouts.
- Operable: Websites must function with different input methods, including keyboard convenience. Ensure users can navigate with the tab key or access visible skip links.
- Understandable: Content and navigation should be easy to comprehend. Clear labels, logical page elements, and consistent page titles help create an accessible design.
- Robust: Websites must be compatible with various assistive devices like screen readers or speech input software and should remain functional even as technologies evolve.
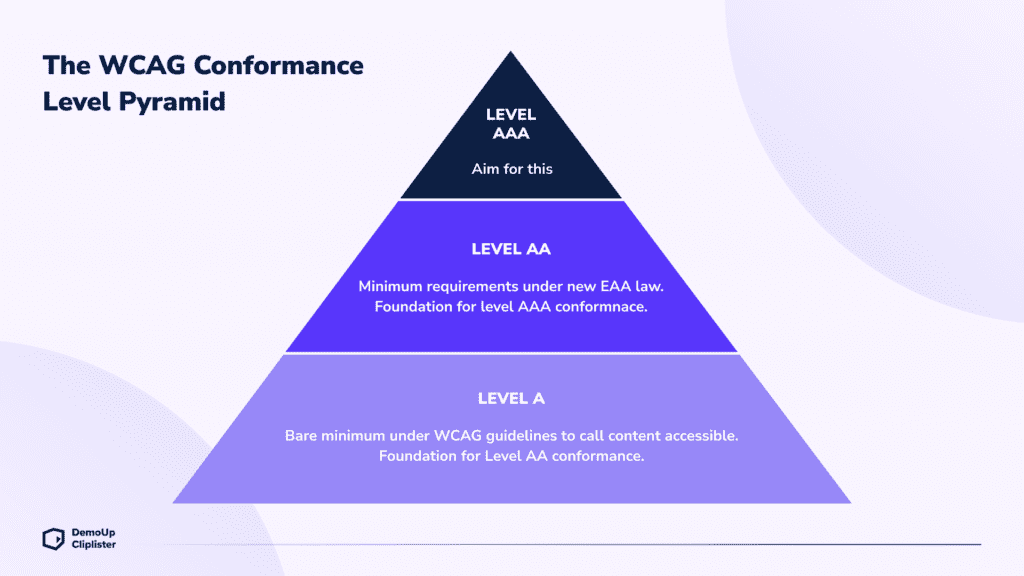
How WCAG Levels Impact Websites
WCAG also outlines different levels of compliance: A, AA, and AAA.
- Level A: The minimum standard for web accessibility. It addresses fundamental barriers that prevent disabled users from accessing the site’s content.
- Level AA: The most common target for businesses and a requirement for the European Accessibility Act (EAA). It ensures a more inclusive experience, addressing issues like colour contrast ratios, alternative text, and user-friendly navigation.
- Level AAA: The highest level of compliance is not always achievable for all types of web content but is ideal for those aiming to deliver the most accessible experience possible.
Accessibility Tools and Resources
Fortunately, there are numerous tools to help assess and improve your website’s accessibility. WAVE and Lighthouse are automated tools that evaluate websites based on accessibility standards.
They can identify issues such as missing alt text, accessibility HTML tags, or improper ARIA attributes for interactive elements.
Another prime example of a valuable resource is the World Wide Web Consortium’s (W3C) guidelines on web content accessibility, which offer comprehensive solutions for making accessible websites.
These resources are crucial for conducting an accessibility audit and ensuring your site complies with accessibility requirements.

EAA Compliance on Autopilot
Make sure your media assets are fully compliant with our EAA modules.
Common Web Accessibility Challenges
Creating an accessible website is not without its challenges. Many businesses struggle with things like:
- Poor colour contrast: Ensuring the text is legible against its background is vital, especially for users with other visual impairments.
- Keyboard navigation issues: If a site is not navigable using only a keyboard, access is limited for those who cannot use a mouse due to fine motor control disabilities.
- Non-semantic HTML: Using improper HTML for page elements can make it difficult for assistive technologies, like screen readers, to interpret the website content correctly.
Legal Implications of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with accessibility standards can have serious consequences. Under the European Accessibility Act (EAA), failure to provide an accessible website could lead to penalties or legal actions.
This is especially important for e-commerce businesses, ensuring their web pages cater to all users, including those with disabilities. Additionally, offering an accessibility statement on your website can further demonstrate your commitment to inclusivity and compliance.
Global Standards Beyond EAA
While the EAA is specific to Europe, its standards align with other global regulations, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in the US and the Accessible Canada Act.
Meeting these international standards helps create a more inclusive digital world and can make your site more appealing to a global audience.
Accessible website examples like the BBC website demonstrate how businesses can design with both accessibility and usability in mind, making their digital spaces welcoming to all.
Best Practices for Designing Accessible Websites
Creating accessible websites ensures all users, including those with disabilities, can fully interact with your content.
By following accessibility guidelines and best practices, you enhance the user experience and align with the European Accessibility Act (EAA).
Perceivable Content
One of the critical elements of accessible websites is ensuring content is perceivable for everyone, including those who use assistive technologies like screen readers.
Start by providing alt text for all images. Alt text offers an alternative for users who cannot see the picture.
For example, instead of labelling a button with an image alone, describe its function with meaningful alt text, like “Search function” or “Download brochure.” This way, everyone can access the functionality of your site.
For video content, adding captions is essential. Captions not only assist individuals who are hard of hearing, but also benefit users in noisy environments.
If you have videos without captions, you’re missing a crucial part of making your accessible content reach a broader audience. A great example is adding captions to tutorial videos or explainer clips on your site.
Operable Features
A core principle of accessible web design is ensuring users can navigate your site without relying on a mouse. Keyboard navigation allows users with mobility issues to quickly move through your website.
Every interactive element, like buttons, links, and search bars, should be accessible via keyboard. Implementing features such as “skip to content” links and focusing on logical page design helps users navigate without barriers.
Testing for keyboard navigation is simple but crucial. Ensure every part of your site is accessible via the Tab button and that interactive elements have a visible focus state, such as a border or background highlight.
It’s one of the most straightforward accessibility solutions yet the most overlooked.
Understandable Content
Clear, concise language is another vital aspect of website accessibility. When you write for your audience, keep sentences short and avoid complex terms.
This approach benefits users with cognitive disabilities and improves overall readability. For example, instead of saying “optimise,” try “improve” or “make better.”
Also, ensure consistent page layout and navigation. Users shouldn’t have to relearn how to navigate your site on each visit. Consistent placement of navigation bars, buttons, and search functions across all pages helps users orient themselves easily.

How Accessible is Your Content? Find Out with This Free Checklist!
Download NowRobust Design
To ensure a truly accessible website, your design must work seamlessly with assistive technologies like screen readers, voice commands, and accessible rich internet applications (ARIA).
Use semantic HTML to structure your pages, making it easier for assistive tools to interpret and convey your content to users.
Elements like aria attributes also enhance accessibility by providing context to screen readers about your website’s buttons, forms, and other interactive parts.
Testing with Real Users
No matter how well-designed your site seems, real-world testing with users who rely on accessibility features is indispensable.
These users can identify issues that automated devices or developers might overlook. Involve users who rely on screen readers, keyboard usage, or magnifiers in your testing process. They can highlight accessibility issues that could make your site more complicated.
Mobile Accessibility Considerations
It’s important to remember that accessible sites must also be mobile-friendly. Many users access websites on their phones, so your mobile site must offer the same level of digital accessibility.
Optimising for mobile includes ensuring that touch targets (like buttons) are large enough to press easily, increasing line spacing to make the text more readable, and ensuring the page adjusts to different screen sizes.
Additionally, pay attention to contrast. Text on mobile devices can sometimes be more challenging to read, especially in bright environments. High-contrast text and backgrounds can improve your mobile version’s visual impact and usability.
Integrating Accessibility in Development Processes
Finally, make website accessibility a priority from the beginning of your development process. Rather than treating accessibility as an afterthought or one-time audit, make it a continuous part of your workflow.
Regular accessibility audits should be scheduled, ensuring that new updates or features align with World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) guidelines.
Using automated methods and regular testing with real users ensures that your own website’s accessibility evolves alongside changes to your site. For example, testing how updates to your search bar or page title affect usability is an excellent way to catch any issues early.

EAA Compliance on Autopilot
Make sure your media assets are fully compliant with our EAA modules.
The Benefits of Web Accessibility for E-Commerce
Creating an accessible website is more than meeting compliance—it can significantly benefit your business.
When your site is accessible to everyone, including those with disabilities, you enhance the user experience, expand your market, and boost your SEO performance.
Enhancing User Experience
An accessible website ensures that all users can engage with your content smoothly, regardless of their abilities.
Designing websites with features like high-contrast visuals, screen reader compatibility, and user-friendly navigation helps create a more intuitive experience. An accessibility audit can help you identify and address issues hindering user interaction.
By catering to a diverse range of customers, you ensure that everyone—from those using assistive technology to those with temporary impairments—enjoys a seamless experience, leading to higher engagement and lower bounce rates.
Expanding Market Reach
An estimated 15% of the global population lives with some form of disability. By making your site accessible, you can tap into this often-overlooked segment. Having an inclusive website helps you reach a broader audience.
Real-world web accessibility examples show that businesses embracing accessible design can attract and retain a more diverse customer base.
Offering features like key elements for more straightforward navigation or visually appealing yet functional design ensures your products or services are available to everyone, helping you expand your market reach.
SEO Boost: Improved Search Rankings
Search engines value well-structured websites, and web accessibility goes hand in hand with good SEO practices.
An accessible site tends to have cleaner code, proper heading structures, and meaningful alt text for images. These are critical factors for improving your search engine rankings.
Many accessible website examples showcase how proper coding and design can lead to a significant SEO boost. By improving your site’s structure and usability, you enhance its visibility on search engines, drawing more organic traffic.
Building Brand Loyalty
Making your website accessible sends a powerful message of inclusivity, showing that you care about every customer. By including an accessibility statement on your website, you foster trust with your audience.
Customers who feel valued and accommodated are more likely to stay loyal. Accessible businesses often see improved customer satisfaction and higher retention rates because they create an environment where everyone can interact freely.
This inclusivity fosters a sense of community, crucial to building long-term loyalty.
Legal Protection from Lawsuits
In many regions, including the EU, web accessibility is legally required. Ensuring that your website meets digital accessibility regulations not only helps you avoid accessibility issues, but also protects your business from costly lawsuits.
Keeping your site compliant with regulations through regular accessibility audits can shield you from legal troubles while promoting fairness in digital spaces.
Future-Proofing Your Website
As regulations surrounding web accessibility evolve, it’s essential to be proactive. Creating an accessible website now ensures you’re ready for future standards.
By building with an accessible design, your site will meet current and upcoming regulations, protecting your long-term investment.
It’s a future-proof strategy that saves you the hassle of costly updates later on.
Financial Benefits: ROI from Accessible Design
Making your website accessible isn’t just the right thing to do—it’s a wise financial decision. Businesses prioritising accessible layouts often see a return on investment (ROI) through increased market reach, improved SEO, and stronger customer loyalty.
With more users able to interact with your web page and fewer barriers to access, you’ll likely see more conversions and sales.
The benefits of inclusivity extend beyond compliance and goodwill—they directly impact your bottom line.
How to Ensure Your Website is EAA Compliant
The European Accessibility Act (EAA) sets clear guidelines to make websites accessible to all users, including people with disabilities. Achieving EAA compliance is not just about meeting legal requirements; it also opens your business to a broader audience and enhances the user experience.
As we move towards the 2025 compliance deadline, here’s how you can ensure your website meets these essential standards.

How Accessible is Your Content? Find Out with This Free Checklist!
Download NowConduct Accessibility Audits
The first step towards compliance is conducting a thorough accessibility audit of your website. Accessibility tools like WAVE and Lighthouse can help identify gaps in your site’s accessibility.
These tools analyse your website’s structure, highlighting issues like missing alt text for images, improper use of headings, and lack of keyboard usage support. However, remember that automated devices only detect part of the problem.
For example, WAVE might flag missing descriptions for images, but it won’t tell if they are meaningful to someone using a screen reader. Therefore, while these tools are crucial, pairing them with manual checks is equally essential to catch nuances automated systems may miss.
Develop an Accessibility Roadmap
With the 2025 deadline for full EAA compliance approaching, it’s crucial to have a clear strategy. Creating an accessibility roadmap helps you prioritise and plan the necessary improvements to your website.
This roadmap should include immediate fixes based on your initial audit, medium-term goals, like redesigning your navigation system to be more inclusive, and long-term objectives such as ensuring new features comply with accessibility rules from the start.
Start by immediately outlining quick wins you can address—like fixing broken links or adjusting colour contrast. Then, plan for more complex updates, such as improving the accessibility of interactive features like forms and chatbots.
Use Automated and Manual Testing
Testing is vital to ensuring accessibility, requiring both automated and manual methods. Automated testing tools like Lighthouse can quickly identify obvious accessibility issues but often miss more subtle challenges.
For instance, a tool may confirm that a keyboard is accessible, but a manual check is needed to verify if the button’s function is clear to someone using a screen reader.
Manual testing also allows you to experience your website like someone with disabilities. This includes navigating your site using only a keyboard, trying different screen readers, or even reducing the contrast on your screen to simulate low vision.
Train Your Development Team
Your development team plays a pivotal role in achieving and maintaining accessibility. Ensure your team understands the importance of accessibility and is trained to integrate it into every stage of the development process.
This goes beyond just following guidelines; it’s about fostering an inclusive mindset. Developers should be familiar with coding practises that support accessibility, such as semantic HTML, which helps users who rely on assistive technologies, like screen readers, to better understand the structure of your content.
It’s also helpful to appoint an accessibility champion within your team who keeps up with the latest accessibility trends and regulations and can help guide others.
Stay Up-to-Date with Changing Regulations
Accessibility regulations and guidelines are constantly evolving. Staying informed about these changes ensures your website remains compliant over time.
Subscribe to updates from organisations like the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and monitor changes to the website content accessibility regulations. These guidelines are frequently updated to reflect new standards and technologies.
For example, with the rise of voice-activated assistants, websites may soon need to consider how they interact with voice commands.
Monitor and Maintain Accessibility
Accessibility is not a one-time project. Websites undergo constant changes—from new product listings to feature updates—so you must monitor accessibility regularly.
Use automated devices to schedule periodic audits and have your team perform manual checks whenever significant updates are made. It’s also a good idea to gather feedback from users with disabilities to identify any new barriers that may have arisen after changes.
For example, a retail website might add a new checkout feature that, while technically functional, isn’t easily accessible to users relying on screen reading software. Regular checks help you catch these issues early and make necessary adjustments.

EAA Compliance on Autopilot
Make sure your media assets are fully compliant with our EAA modules.
Conclusion
To meet the June 2025 EAA deadline, businesses must start integrating accessibility into their web development and design processes now.
By following best practices, you’ll gain more than just compliance—you’ll unlock benefits like improved SEO, more robust legal protection, and better user engagement. When users can access your content easily, it boosts satisfaction and loyalty.
Look to accessible website examples for inspiration, and remember, making your site accessible is an ongoing effort that pays off long-term. Embrace accessibility today and position your business for success tomorrow.
For more on accessibility, digital asset management, or e-commerce content, check out our blog.
To see our full product portfolio, return to the homepage.
Better Content. More Sales.

Fill out the form to discover our end-to-end eCommerce content solutions for brands & shops




